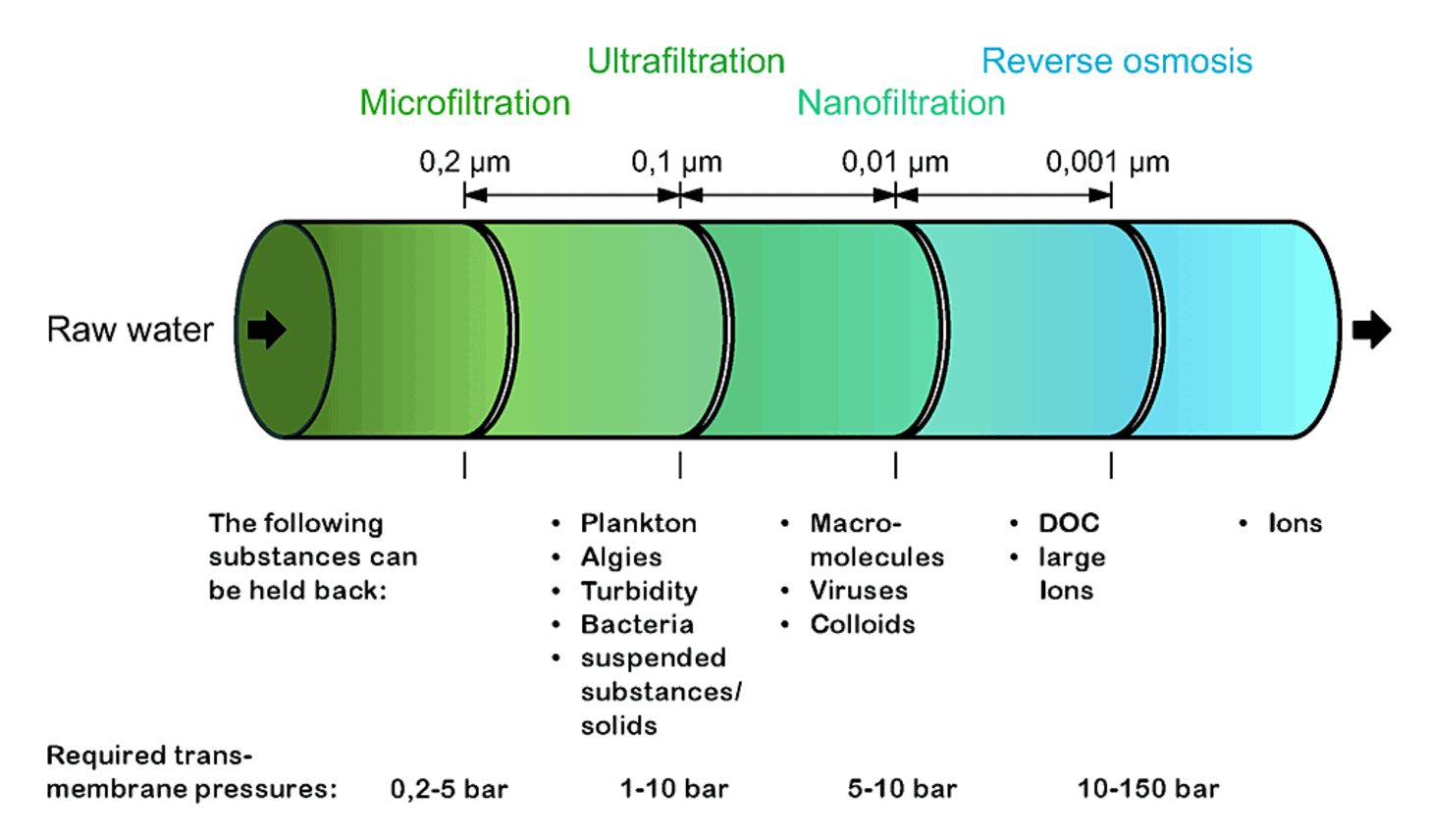
Membrane processes in water treatment refer to processes in which substances are separated from aqueous solutions using membranes. Microfiltration (MF) and ultrafiltration (UF) are primarily used to remove suspended substances such as particles or microorganisms. Nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO), on the other hand, are used to separate dissolved substances such as salts.
Differences and structure of the membranes
Microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes act as purely mechanical “fine sieves”. They are made either of ceramic or of porous, artificially produced polymer films (membranes) with precisely defined pore diameters. The actual separation layer is applied to a carrier material, which—depending on the design—is made of polymers or ceramics.
Dense, semi-permeable membranes are used in nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. In these processes, separation occurs through diffusion and transport of solutes through the membrane. In all cases, the driving force is the applied differential pressure. While differential pressures of up to 2 bar are sufficient for microfiltration and ultrafiltration, low-pressure nanofiltration requires up to 8 bar. Reverse osmosis, on the other hand, requires differential pressures of up to 60 bar.
Structure of porous membranes
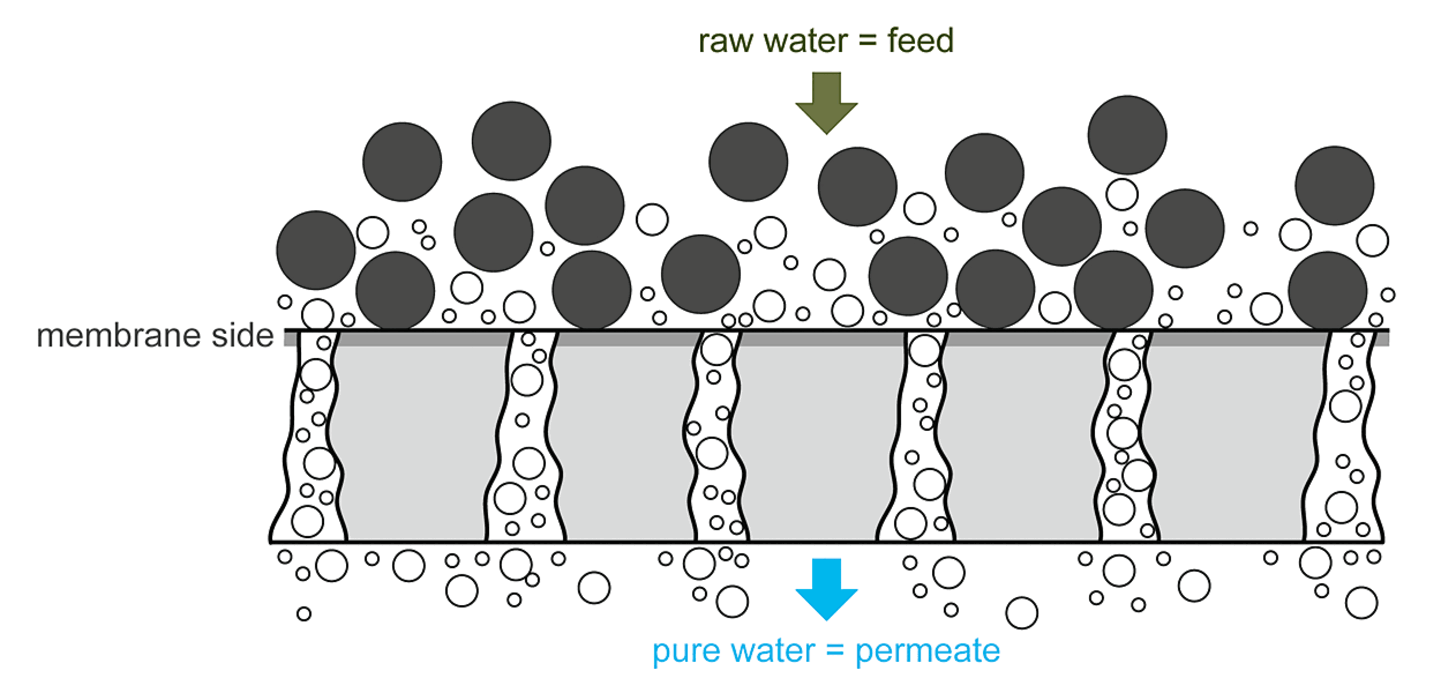
The active membrane layer is extremely thin and is located on the side facing the raw water (feed). By far the largest part of the membrane consists of the support material, which provides the mechanical structure and the necessary strength. For proper function, it is crucial that the pores become larger toward the permeate side; otherwise, there is a risk of irreversible clogging.
The purified water obtained downstream of the membrane is referred to as filtrate or permeate, while the retained substances are referred to as concentrate or retentate.
Materials and types of membranes
Modern membranes are composed of either polymers (e.g., polyethersulphone, PVDF) or ceramic materials (e.g., aluminium oxide, silicon carbide).
While ceramic membranes involve higher manufacturing costs than polymer alternatives, they offer superior chemical resistance and significantly higher permeability.
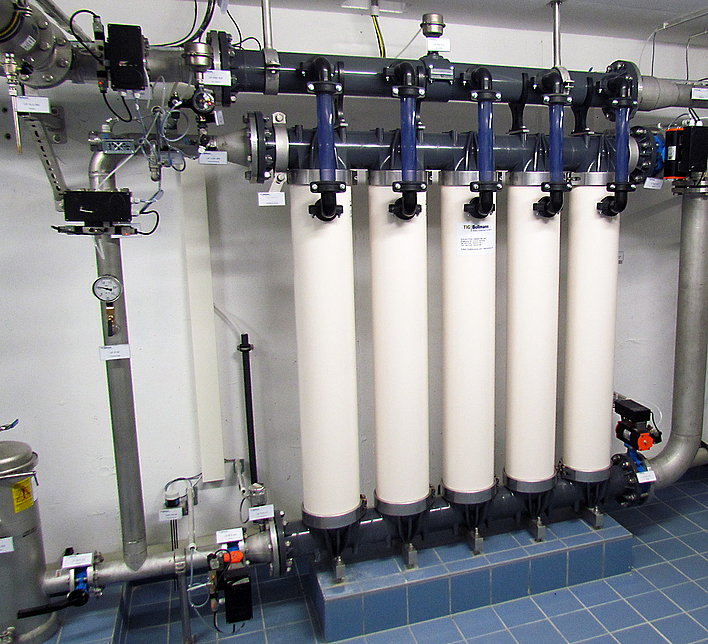
The membranes are fabricated either as capillaries (hollow fibre membranes) or as flat-sheet membranes. For technical applications, these membranes are integrated into larger units; depending on the configuration, these are classified as tubular, spiral-wound, plate-and-frame, or pillow modules. Hermetic separation between the raw water (feed) and treated water (permeate) sides is ensured by specialized sealing compounds, typically based on polyurethane resins.
Depending on the required performance, a membrane system usually consists of a large number of identical modules, which are operated simultaneously in parallel.
Method of operation
Membrane systems are operated using either the cross-flow process (tangential flow filtration) or the dead-end process (dead-end filtration).
Cross-flow Operation
In this process, the membrane surface is continuously scoured by a tangential flow. This cross-flow minimizes the formation of cake layers (fouling) and ensures stable filtration conditions. While this allows for a higher flux (filtration rate), it involves higher energy consumption due to the requirement for a circulation pump.
Dead-end Operation
This mode of operation is analogous to conventional filtration, where the entire volume of raw water is pressed perpendicularly through the filter medium. Since there is no continuous recirculation, the process is more energy-efficient and represents a more cost-effective solution for many applications.
Planning and Design
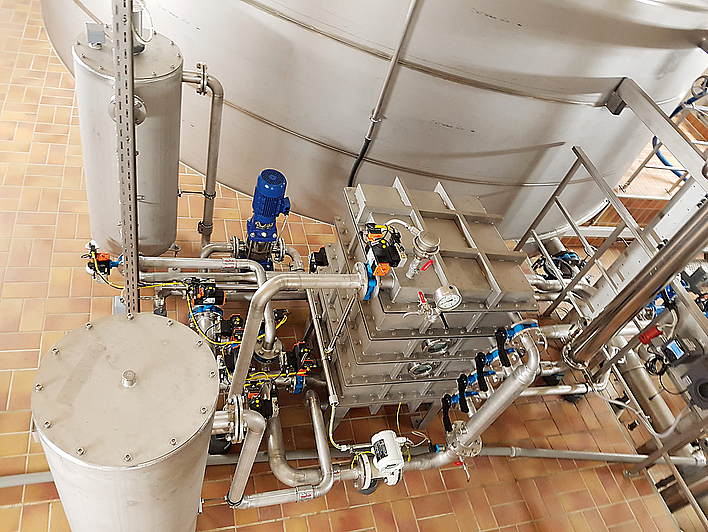
The efficiency of a membrane system depends crucially on meticulous system design and precisely tailored pre-treatment. Both the selection of module types and the operating mode must be aligned with the specific raw water characteristics and the required purification standards.
We design and build plants for all membrane prosesses. To this purpose we avail ourselves of state-of-the-art knowledge and see great opportunities in the application of combination processes, such as ozone-supported membrane filtration and chemicalfree regeneration with use of ozone.
Send us your requirements - we would also be very happy to work for you.